Trigeminal Neuralgia or also known as Tic Douloureux is a sudden and severe facial pain. The term neuralgia refers to severe pain along the course of a nerve due to nerve irritation or damage. Trigeminal Neuralgia affects the trigeminal nerve which is one of the most wide-reaching nerves in the head.
This pain is often described as sharp shooting pain or an intense electric shock, causing it to be one of the most known excruciating pain. It usually happens in short and unpredictable attacks that can last from a few seconds to about 2 minutes. The attacks stop as suddenly as they start. The pain can be triggered by simple activities such as brushing teeth, washing your face, shaving, or putting on makeup. Even a light breeze against the face might set off the pain.
In most cases, trigeminal neuralgia affects just one side of the face with the pain usually felt in the lower part of the face. Very occasionally the pain can affect both sides of the face although not usually at the same time. When that happens, it is called Bilateral Trigeminal Neuralgia.
So what causes Trigeminal Neuralgia?
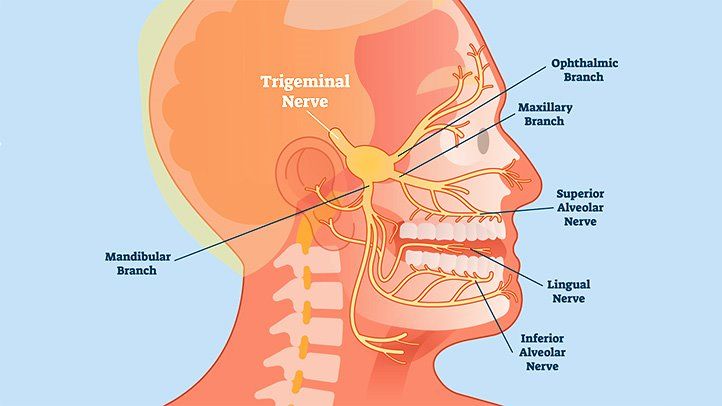
There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves in the human head. The trigeminal nerves are among these pairs which allow sensations to be felt in the face. One nerve runs down each side of the head.
Each trigeminal nerve splits into three branches which control the feeling for different parts of the face.
- The ophthalmic branch controls the eye, upper eyelid, and forehead.
- The maxillary branch affects the lower eyelid, cheek, nostril, upper lip, and upper gum.
- The mandibular branch runs the jaw, lower lip, lower gum, and some muscles used for chewing.
The disorder can affect any of the three nerve branches which means that the pain can be felt from the forehead to the jaw.
The cause of trigeminal neuralgia often starts with irritation of the trigeminal nerve caused by a tumor, tangle of arteries, or blood vessels pressing on the nerve which damages the protective coating around the nerve called the myelin sheath. Certain diseases such as multiple sclerosis can also injure the myelin sheath.
Physical therapy can help relieve the severity of symptoms with Trigeminal Neuralgia. To reduce muscle spasms, manual therapy alongside heat therapy will be applied to the neck and trapezius muscle. Relevant isometric neck exercises and pain-free range of motion exercises (neck flexion, extension, and side-flexion) will also be prescribed by your therapist. Relaxation techniques which include deep breathing exercises will also be taught. If in doubt, seek professional advice.
Check out our popular articles: Diastasis Recti, Tight Back Muscles, Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Dysfunction, Tennis Elbow, Wrist Tendon Injury, Sciatica, Whiplash, Hernia, Herniated Disc (Slipped Disc).